According to many experts, chronic prostatitis is an inflammatory disease caused by an infection with a possible addition of autoimmune diseases, characterized by damage to the parenchymal and interstitial tissue of the organ.The disease has been known in medicine since 1850, but even today it remains poorly understood and difficult to treat.Chronic bacterial (6 - 10%) and non-bacterial (80 - 90%) prostatitis are the most common and socially significant inflammatory diseases in men, significantly reducing their quality of life.The disease is recorded mainly in young and middle-aged people and is often complicated by disorders of copulative and reproductive functions (decreased potency, infertility, etc.).The disease is recorded in men in 8 to 35% of cases aged between 20 and 40 years.
The cause of bacterial prostatitis is the pyogenic flora that penetrates the gland through the urethra or the lymphogenic and hematogenic pathways.The etiology of non -bacterial chronic prostatitis and its pathogenesis remain unknown.Mainly affects men over 50 years old.
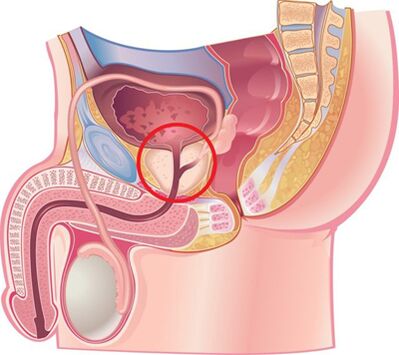
Reasons for the development of the disease
Chronic prostatitis is currently considered a polyetiological disease.There is the opinion that the disease occurs due to the entry of an infection in the prostate and then the pathological process continues without its participation.This is facilitated by a number of non -infectious factors.
Infectious factors for the development of chronic prostatitis
In 90% of cases, pathogens penetrate urethra iron as a result of acute or chronic prostatitis.Cases of asymptomatic transport are observed.The course of the disease is influenced by the state of the protective forces of the human body and the biological properties of the pathogen.It is assumed that the transition from acute to chronicle prostatitis occurs due to the loss of elasticity of the tissue due to the excess of fibrous tissue products.
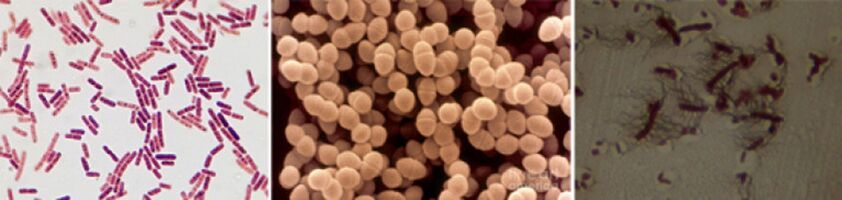
Among the causative agents of chronic prostatitis, the following pathogens are found:
- In 90% of cases, the disease reveals Gram -negative bacteria such as Escherichia coli (E. coli), Enterococcus faecalis (Fecal Enterococcus), less often - Pseudomonas aeruginosa, Klebsiella spp., Proteus spp., Prototo spp.Pseudomonas aeruginosa, Enterobacter Aerogenes and Acinetobacter spp.Chamber-positive bacteria from enterosococci, streptococci, and staphylococci are rare.
- The role of coagulases-negative staphs, urereaplasma, chlamydia, trichomonia, gardnerell, anaerobic bacteria and fungi of the genre Candida were finally clarified.
Prostate infection penetrates in several ways:
- The upward path is most likely to be proven by a frequent combination of prostatitis and urethritis.
- Hematogenous prostatitis develops with the penetration of infection into the gland with a blood flow, which is observed with chronic tonsillitis, sinusitis, periodontitis, pneumonia, cholecystitis and cholangitis, purulent skin diseases, etc.
- Chronic prostatitis in contact develops with urethritis and strictures of the urethra, when the infection penetrates the ascending gland with the current of urine, with purulent infections of the kidneys, canalicular epipiditis, defentitis and funiculitis, inspiring diagnostic and therapeutic retransmission (catheterization, rentocage, rentocation, rentocation,renting, renting of renicultures, inspiring diagnosis and therapeutic retransmission.
- The infection lymphogenically penetrates the prostate with proctus, thrombophlebitia of hemorrhoidal veins, etc.
Non -infectious factors in the development of chronic prostatitis
Chemical factors
According to experts, the main role in the development of chronic prostatitis belongs to intraseprostatic reflux urine when urine is released from the urethra into the iron, which leads to a violation of the emptying of the prostate and seminal vesicles.
With the disease, vascular reactions develop to the edema of the organ, the nervous and humoral regulation of the tone of the smooth muscle tissues of the urethra and the activation of alpha are disturbed1–As -adrenoreceptors cause the development of dynamic obstruction and contribute to the development of new intraprostatic reflux.
Urates contained in urine, with reflux, lead to the development of a "chemical inflammatory response".
Hemodynamic disorders
Support chronic inflammation of circulatory disorders in the pelvic and scrotum organs.Stagnation develops in people who carry a sedentary lifestyle, for example, for drivers, office staff, etc., with obesity, sexual removal, sexual dysmetrization, frequent hypothermies, mental and physical overload.Keeping the process inflammatory, taking spicy and spicy foods, alcohol and smoking, etc.
Other factors
There are many other factors that support the chronic inflammatory process in the prostate.These include:
- Hormonal.
- Biochemistry.
- Violations of the immune response.
- Autoimmune mechanisms.
- Infectious and allergic processes.
- Characteristics of the structure of the prostate glands, leading to the difficulty of total drainage.
It is often not possible to establish the causes of chronic prostatitis.
Prostatitis Classification
According to the classification proposed in 1995 by the United States National Institute of Health, prostatitis is divided into:
- Clear (category I).It is 5 - 10%.
- Chronic bacterial (category II).It is 6 - 10%.
- Non -bacterial inflammatory chronic (category IIIA).It is 80 - 90%.
- Chronic non-inflammatory non-inflammatory (category IIIB) or chronic pelvic pain syndrome.
- Chronic prostatitis detected by chance (category IV).
Signs and symptoms of chronic prostatitis
The course of chronic prostatitis is long but not monotonous.Periods of exacerbation are followed by periods of relative calm, which occur after anti -inflammatory therapy and complex antibacterial therapy.
The development of chronic bacterial prostatitis is often preceded by urethritis of a bacterial or gonorrheal, non-bacterial nature - circulatory disorders in the pelvic and scrotal organs (hemorrhoids, varicoceles, etc.), sexual excesses.
Patients with chronic prostatitis have many complaints.They have been going to the doctor for years, but very rarely are they checked for prostate disease.About a quarter of patients have no complaints or the disease occurs with few clinical symptoms.
Complaints of patients with chronic prostatitis can be divided into several groups.
Urinary disorders associated with urethra narrowing:
- Difficulty urinating initially.
- Weak flow of urine.
- Intermittent or dripping urination.
- Feeling of incomplete emptying of the bladder.
Symptoms caused by irritation of nerve endings:
- Frequent urination.
- The desire to urinate is acute and strong.
- Urination in small portions.
- Urinary incontinence during the urge to urinate.
Pain syndrome:
- The intensity and nature of the pain varies.
- Location of pain: lower abdomen, perineum, rectum, groin and lower back, inner thighs.
Sexual dysfunction:
- Pain in the rectum and urethra during ejaculation.
- Slow erection.
- Loss of orgasm.
- Premature ejaculation, etc.
Of the nervous system: neurotic disorders in the form of attachment of patient care in their health.
Signs and symptoms of non -bacterial chronic prostatitis
Chronic pelvic pain syndrome in men (SDPC) occurs with the usual symptoms of chronic prostatitis, but there are no bacteria in the 3rd portion of the urine and prostate secretions when examined.Chronic non -bacterial interstitial cystitis, rectum diseases, pelvic floor spastic myalgia syndrome and functional prostate lesions caused by organ innervation disorders and their hemodynamics can simulate CPPs.
If the neurovegetative function is impaired, there is atony and violation of the innervation of the gland, which manifests itself by difficulties in the rapid and complete closure of the light of the urethra.In this case, after urination, the urine continues to be released a drop for a long time.In these patients, the study reveals instability and increased excitability, which manifests itself by increased sweating and excitability of cardiac activity, changes in dermographism.
Complications of the disease
The long course of chronic prostatitis is complicated by disorders of sexual and reproductive functions, the development of diseases such as vesiculitis and epididymitis, as well as organ sclerosis.Organ sclerosion worsens microcirculation and local urodynamics, as well as the results of surgical interventions.Fibrosis of periumetral tissues leads to the development of urination disorders.
Diagnosis
Due to the fact that there are many reasons for the development of chronic prostatitis, a whole complex of diagnostic studies is used to diagnose.The success of treatment depends on the correct determination of the causes of the disease.The diagnosis of chronic prostatitis is based on the following data:
- Classic triad of symptoms.
- A complex of physical methods (rectal examination of prostate fingers).
- A laboratory method complex (urine analysis and prostate microscopy, sowing and determining the sensitivity of microflora to antibacterial drugs, general urine and blood analysis).
- To detect gonococci, bacterioscopy stains urethra, PCR and serological methods (to detect ureaplasma and chlamydia).
- Uroflometry.
- Prostate biopsy.
- An instrumental method complex (ultrasound).
- Determination of the patient's immune status.
- Determination of neurological state.
- If the treatment is ineffective and complications are suspected, computed tomography and magnetic resonance imaging, blood culture, etc. are performed.
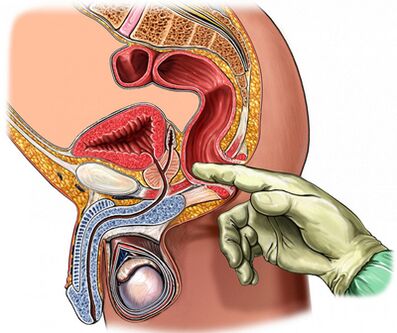
Palpation of the prostate
Of primary importance in diagnosing the disease is palpation of the prostate, which increases during the period of exacerbation and decreases during the period of subsidence of the inflammatory process.In chronic prostatitis, during the period of exacerbation, the gland becomes swollen and painful.
The consistency of the organ may be different: areas of softening and hardening are palpated and certain areas of retraction.By palpation it is possible to evaluate the format of the gland, the state of seminal tubers and surrounding tissues.
The transrectal digital examination process is combined with the collection of glandular secretions.Sometimes it is necessary to obtain the secretion from each lobe separately.
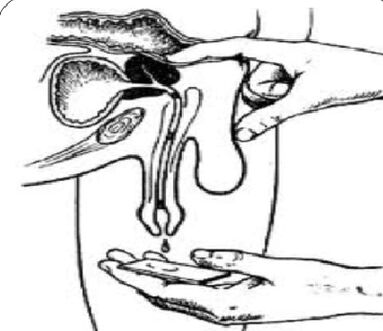
Analysis of a sample of 3 cups of urine and prostate secretion
The “gold standard” in the diagnosis of chronic prostatitis are:
- Collecting the first portion of urine.
- Collection of the second portion of urine.
- Obtaining glandular secretions through massage.
- Collection of the third portion of urine.
Then the microscopic and bacteriological examination of the material is performed.
For prostate inflammation:
- Microbial Count (UFC) exceeds 103/ml (104/ml for epidermal staphylococci), but should not be neglected by a small number of microbes calculated by tens and hundreds.
- The presence of 10 to 15 leukocytes in the field of view detected by microscopy is a generally accepted criterion for the presence of an inflammatory process.
The secret of prostate and third parts of the urine is subjected to microscopic and bacteriological studies:
- In chronic bacterial prostatitis, an increase in the number of leukocytes in the secretion of the gland is observed and in the third portion of post-massage urine, bacteria are released (mainly intestinal group).
- With non-bacterial prostatitis, an increase in the number of leukocytes in the secretion of the gland is observed, but the microflora is not detected.
- With CTB, there are no increased amounts of white and microflora blood cells.
The normal indicator of prostate secretion:
- Leukocytes less than 10 in the field of vision.
- Lecithin grains are a large number.
- There is no microflora.
In chronic prostatitis in the secretion of the prostate gland, one finds:
- The number of leukocytes is large with the exception of 10 to 15 in the field of vision.
- The amount of lecithin grains is reduced.
- The pH of the secretion is displaced to the alkaline side.
- The content of acid phosphatase is reduced.
- Lysozyme activity is increased.
Obtaining negative results of prostate secrecy first does not prove the lack of an inflammatory process.
The value of the prostate secret test remains.Usually, during crystallization, a characteristic pattern is formed in the form of a fern leaf.In case of violation of prostatic secret aggregation properties, this pattern does not form what occurs with changes in the androgen hormonal background.
Ultrasound study
In case of suspected prostate disease, an ultrasound examination of the gland (transient ultrasound), the kidneys and bladder is ideal, which allows to determine:
- Volume and dimensions of the gland.
- The presence of calculation.
- The dimensions of the seed bubbles.
- The condition of the bladder walls.
- The amount of residual urine.
- Clothing structures.
- Another type of pathology.
Other prostate research methods
- The state of urodynamics (study of urine flow rate) is easily and simply determined using a study such as uroflowetry.With the help of this study, it is possible to timely detect signs of infravidal obstruction and carry out dynamic observation.
- Punch biopsy is performed in case of suspected abscess, benign hyperplasia and prostate cancer.
- In order to clarify the causes of the development of infravezicular obstruction, radiological and endoscopic examination is performed.
- With a long inflammatory process, it is recommended to perform urethroscopic surgery.
Differential diagnosis
Chronic Prostatis Should Be distinguished from vesiculoprofostasis, Autonomic Prostatopathy, Stagnant Prostatis, Pelvic Bottom, Psychoneurological Disorders, Pseudo -Detision, Reflex Sympather Dystrophy, Inflammatory Diseases of Other Organs: InterstitialCystitis, Osteitis of the Longitudinal Art, Sexual Dysphuncture, Sexual Dysfunction, Sexual Dysfunction, Sexual Dysfunction.Bladder neck hypertrophy, urethra stenosis, tuberculosis, prostate and bladder cancer, urolithiasis, chronic epipidimite, inguinal hernia.
Treatment of chronic prostatitis
Treatment of chronic prostatitis should begin with a change in the patient's lifestyle and nutrition.
In the treatment of the disease, drugs are used simultaneously that affect different bonds of pathogenesis.
The main directions of therapy:
- Eliminating causal microorganisms.
- Anti -inflammatory therapy.
- Normalization of blood circulation in the prostate and pelvic organs.
- Normalization of adequate drainage of prostatic Ainus.
- Normalization of the hormonal profile.
- Prevention of organ sclerosion.
For the treatment of chronic prostatitis, medicines from the following groups are used:
- Anti-bacterial.
- Anticholinergic.
- Vasodilators.
- Alpha1-Adren -block.
- Inhibitors 5 alpha reductase.
- Cytokine inhibitors.
- Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs.
- Angioprotectors.
- Immunomodulators.
- Preparations affecting urate exchange.
Antibiotics in the treatment of bacterial chronic prostatitis
Antibacterial therapy should be carried out taking into account the sensitivity of the detected microorganisms to antibiotics.If the pathogen is not detected, empirical antimicrobial treatment is used.
The drugs of choice are generation II fluoroquinolones - IV.They quickly penetrate the gland tissues with common use methods, show activity against a large group of gram -negative microorganisms, as well as urereaplasm and chlamydia.In case of antimicrobial treatment failure, it should be assumed:
- Microflora Polyurezncy,
- short (less than 4 weeks) courses of treatment,
- Incorrect selection of the antibiotic and its dosage,
- changes in the type of pathogen,
- The presence of bacteria living in the prostate ducts, covered with a protective extracellular membrane.
The duration of treatment should be at least 4 weeks with subsequent bacteriological control.In case of preservation in the 3rd part of the urine and the secret of the Bacteriuria Prostate, more than 103Correspondence of a re-antibacterial therapy for a period of 2 to 4 weeks is prescribed.
Cytokine inhibitors in the treatment of chronic prostatitis
Cytokines are glycoproteins secreted by immune cells and others under inflammatory reaction conditions and an immune response.They are an active part in developing a chronic inflammatory process.
Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory medications
Non -esteroid anti -inflammatory drugs have an anti -inflammatory effect, reduce pain and fever.They are widely used in the treatment of chronic prostatitis in the form of tablets and suppositories.The most effective is the rectal path of the introduction.
Immunotherapy
In the treatment of chronic bacterial prostatitis, in addition to antibiotics and anti-inflammatories, immunomodulatory agents are used.The most effective is the rectal route of its introduction.The immunomodulator is widely used, which increases the functional activity of phagocytes, which contributes to more effective elimination of pathogens.
Alpha blockers in the treatment of chronic prostatitis
It has been established that alpha-1 adrenergic shoes normalize the tone of the smooth muscles of the prostatic part of the urethra, seed bubbles and prostate capsules, which makes the medicines of this group very effective in treating the disease.Alpha-1 adrenergic shoes are used in patients with pronounced urination disorders in the absence of an active inflammatory process.
With CTB, the treatment period is 1 to 6 months.
5A-Reductase inhibitor in the treatment of abactry prostatitis and CPPS
It has been established that under the influence of the enzyme 5a-reductase, testosterone is converted into the prostatic form 5a-dihydrotestosterone, the activity of which in prostate cells is more than 5 times greater than the activity of testosterone itself, which in elderly people leads to an increase in the organ due to epithelial and stromal components.
Upon taking a 5A-Reductase inhibitor, there is atrophy of the smelling tissue for 3 months, glandular tissue atrophy for 6 months, the secretary function is inhibited, the intensity of pain and the volume of the gland are reduced, the tension and swelling of the organ are reduced.
The role of anti-slab medications in the treatment of chronic prostatitis
With prolonged inflammation in the prostate gland, fibrosis develops, which is manifested by disturbances in microcirculation and urodynamics.To prevent the fibrosis process, anti-sclerotic drugs are used.
Other medications used to treat chronic prostatitis
Along with the medicines described above, the following are used to treat the disease:
- Antihistamines.
- Vasodilators and angioprotectors.
- Immunosuppressants.
- Medicines that affect urat metabolism and trisodic citric acid.
Herbal products
Effective in the treatment of prostatitis, the use of the drug in the form of candles containing a biologically active peptide complex isolated from the prostate cattle gland.
Under the influence of the drug:
- Stimulation of metabolic processes in gland tissues.
- Improving microcirculation.
- Reducing edema, leukocyte infiltration, stagnation and pain.
- Prevention of thrombosis in prostate gland venules.
- Increasing the activity of the acinus secretory epithelium.
- Improving sexual function (increased libido, restoration of erectile function and normalization of spermatogenesis).
Massage of the Prostate Gland fingers
A number of researchers say that in chronic prostatitis, finger massage should be used, taking into account known contraindications.
Physiotherapy
The effectiveness of physiotherapeutic procedures in the treatment of prostatitis is not proven today, the mechanism of action has not been scientifically established, adverse reactions have not been studied.
Chronic prostatitis prevention
Starting the prevention of the development of chronic prostatitis, you should know:
- The risk of developing the disease increases over the years.
- Black representatives are more predisposed to the disease.
- A family predisposition to the disease is not excluded.
People with a predisposition to developing chronic prostatitis should be more attentive to their health status.
Tips to prevent the disease:
- Take enough fluids.Frequent urination helps eliminate microflora from the urethra.
- Prevent diarrhea and constipation.
- Follow a balanced diet.Avoid eating foods rich in carbohydrates and saturated fats that lead to weight gain.
- The consumption of substances that irritate the urethra should be limited as much as possible: hot and spicy foods, smoked foods, sauces and seasonings, coffee and alcohol.
- Stop smoking.Nicotine negatively affects the condition of the vascular walls.
- Don't get too cold.
- Be sure to empty the bladder.
- Take an active lifestyle and practice sports.Exercise to strengthen the pelvic muscles, which eliminates the stagnation of venous blood, which in turn maintains the normal functioning of the prostate.
- Have a regular sex life.Avoid prolonged abstinence.The gland must be cleaned of secretions in a timely manner.
- Stay committed to a monogamous relationship.Promiscuous sex increases the likelihood of acquiring sexually transmitted diseases.
- If you have complaints from the genitourinary organs, contact a urologist immediately.